
Synovial joints allow bones to slide past each other or to rotate around each other. Synovial joints achieve movement at the point of contact of the articulating bones. In these joints, the contiguous bony surfaces are covered with articular cartilage and connected by ligaments lined by synovial membrane. Diarthroses are freely movable articulations. As with most other joints, synovial joints achieve movement at the point of contact of the articulating bones.Ī synovial joint, also known as a diarthrosis, is the most common and most movable type of joint in a mammal’s body. They are the most common and most movable type of joint in the body of a mammal. The skull bones are connected by fibrous joints called sutures. These joints have no joint cavity and are connected via fibrous connective tissue. Most fibrous joints are also called “fixed” or “immovable”.
Example: Cranium, pri cartilaginous joint in children and cranial sutures in adults.

What is a fixed joint example?įibrous or fixed joints or Immovable joints: These joints are held together by tough tissue which develops during childhood. There are three different types of fixed joints in the body: sutures, syndesmoses and gomphoses. They are movable joints containing a lubricating liquid called synovial fluid.įixed joints, also called synarthrosis joints, refer to the joints that provide stability to certain areas of the body, such as the joints of the bones of the skull and pelvis. Most of your joints are ‘synovial joints’.

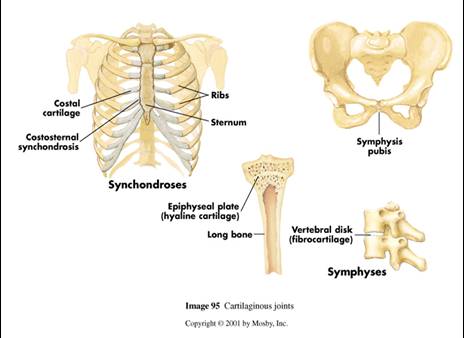
The bones in your skull are held together with fibrous connective tissue. Some of your joints, like those in your skull, are fixed and don’t allow any movement. The joints between the vertebrae and the intervertebral disks are also of this type. In this type of joint, the bones are connected by hyaline cartilage or fibrocartilage. Slightly movable joints are called amphiarthroses. What is the difference between fixed and moveable joints?įixed joints do not allow any movement of the bones, which protects the brain from injury.
MOVABLE JOINTS SERIES
Joints can move in four ways: gliding, in which one bony surface glides on another without angular or rotatory movement angulation, occurring only between long bones, increasing or decreasing the angle between the bones circumduction, occurring in joints composed of the head of a bone and an articular cavity, the long bone describing a series of circles, the whole forming a cone and rotation, in which a bone moves about a central axis without moving from this axis. Joints are also grouped according to their motion: ball-and-socket ( enarthrodial) hinge ( ginglymoid) condyloid pivot ( trochoid) gliding ( arthrodial) and saddle. A diarthrodial joint is one in which the adjoining bone ends are covered with a thin cartilaginous sheet and joined by a joint capsule lined by a synovial membrane, which secretes synovial fluid. An amphiarthrodial joint is one having a fibrocartilaginous disk between the bony surfaces (symphysis), such as the symphysis pubis or one with a ligament uniting the two bones (syndesmosis), such as the tibiofibular articulation. A synarthrodial joint is one in which the two bones are separated only by an intervening membrane, such as the cranial sutures.
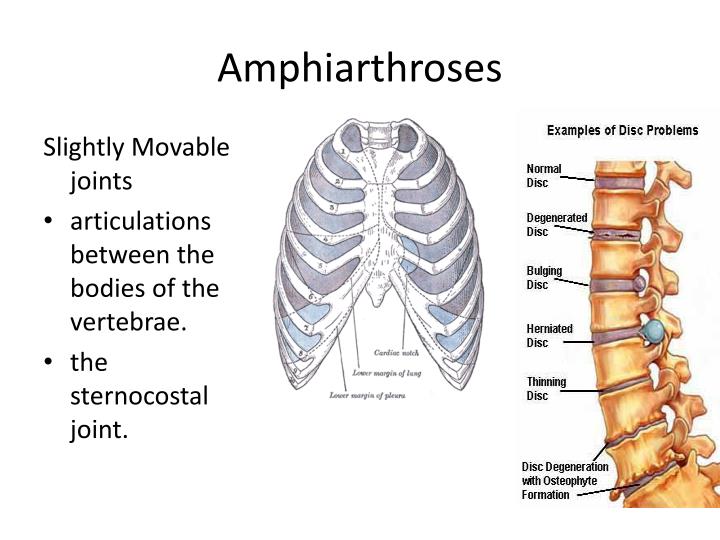
A joint is classified as immovable ( synarthrodial), slightly movable ( amphiarthrodial), or freely movable ( diarthrodial). A joint usually has a thin, smooth articular cartilage on each bony surface and is enclosed by a joint capsule of fibrous connective tissue. Some joints are fixed or immobile attachments of bones other joints allow the bones to move along each other.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
